3D Bioprinting: an additive manufacturing technique
3D Bioprinting: an additive manufacturing
technique
Date:20/12/2022
What is 3D Bioprinting?
A key advancement in contemporary science that has the potential to alter the course of human history is biotechnology. A method known as "bioprinting" promises to produce artificial tissues or organs for the benefit of humanity. The twenty-first century saw a quick rise in three-dimensional printing.This procedure enables the creation of customized tissues and organs from living cells.Additionally, the organ may contain bioactive substances or biomaterials.
Fig:3D printed nose and ear
The scientists had a very difficult time building an organ that could function perfectly inside a human. But in the realm of tissue engineering, scientists and medical professionals have excelled. Again, comparisons between 3D printing and 4D printing, which adds a fifth dimension called time, have been made. This 4D printing, which is essentially an evaluated form of 3D printing, may replicate mechanisms.
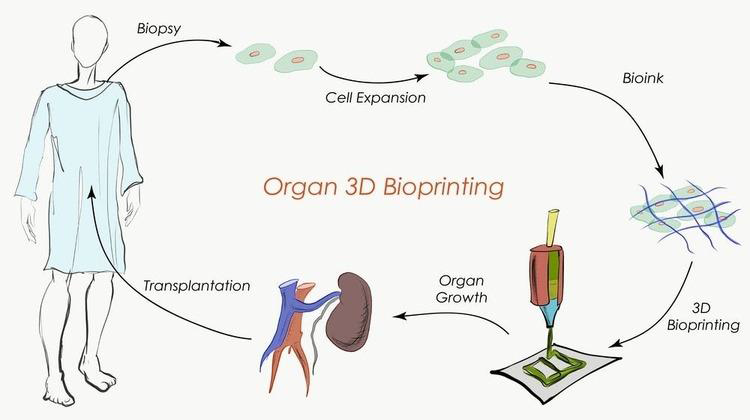
Fig:Process
of Organ 3D bioprinting and it’s
transplantation
Current research and
useage of 3D bioprinting:
• With the use of 3D printing, it is now able to regenerate tissues and organs like the heart, liver, blodder, skin, blood vessels, and lung scaffolds.
• This 3D bioprinting technique can be used to regenerate bone tissue.
• The research field also includes a process called cardiac tissue engineering that addresses heart failure.
• The use of 3D bioprinting in cosmetic surgery is also growing.
• One of its accomplishments is the ability to pattern precise cells and materials.
• It can also explain how the COVID-19 virus spreads among humans and damages our brain tissue.
• Recently, it has been employed in cancer research studies to learn more about the pathophysiology of the disease and its rate of growth.
• Using 3D bioprinting technology, a study team has just created cartilage that can be customized in shape.
• The first human bladder created from a patient's own gene was implanted for the first time in 1999. The researchers at the Wake Forest Institute of Regenerative Medicine accomplished an excellent job.
• Despite the fact that distinct types of tissues need to be produced for both in vivo and in vitro applications, 3D bioprinting technology has made significant progress in human studies.
• Once more, scientists use 3D bioprinting to create corneal, neuronal, and cardiovascular constructions in a variety of animal species.
• A team of Australian scientists has developed a more sophisticated 3D bioprinter that can create exact replicas of human ears. It can be used for surgery by doctors.
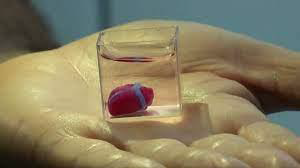
Fig:1st rabbit sized heart invented by scientists from Israel
Advantages:
3D bioprinting technology has made such strides in recent years that it may now be referred to as sophisticated bio manufacturing technology. The use of 3D bioprinting has many benefits. Among them are:
• People's given organs may be rejected if the tissues don't match the patient's or the time of the donation was abused. However, in 3D bio printing technology, a patient's living cell is taken. Organ rejection is therefore not a possibility.
•With the aid of 3D bioprinting, researchers are analyzing tissue engineering and testing it using pharmacological experiments.
•This has made it possible for a variety of studies on some clinical illnesses.Since living cells may be used to create organs, cruel animal testing can be ended.
•Burn sufferers have a chance for recovery.
• The first bio printer, which used bio ink to print any living cells, was created in 2003.It could also print tissues.
• As part of their investigation, scientists are building miniature versions of numerous human organs.
Future prospects:
• In the future, 3D bio printing will make it simple to assist patients who are in need of organ transplants.
• Bioprinting is expressing a wide range of potential in the realm of regenerative medicine.
• Skin tissue that can completely cover burn scars or any other difficulties in the near future can be created via 3D bioprinting without any complications.
Importance:
Over the past ten years, bioprinting has improved and begun to demonstrate its effectiveness in a variety of disciplines, including the biological one. The researchers will concentrate on developing better organoids, applying regenerative techniques, treating diseases, and creating organs from a patient's own cells. Research on this subject must therefore continue.
Reference/Hiperlink:
1.Ozbolat.I.T.
Peng.W.Ozbolat.Veli.( August
2016) Application areas of 3D
bioprinting. Volume
21,
Issue 8, Pages 1257-1271.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drudis.2016.04.006
2.
Jiang,
Wei; Mei, Haiying; Zhao, Shuyan ( 6, June 2021) Volume 17, Number 6. pp.
989-1006(18).
https://doi.org/10.1166/jbn.2021.3078
3.
De.k,Niu.C,Yang.Xi.( march 2022). Bioprinting.
). Evolution of 3D bioprinting-from the
perspectives of
bioprinting companiesVolume 25, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bprint.2022.e00193




Comments
Post a Comment